科研:EMC服务数据在JCR1区ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces发表论文阅读次数 [1638] 发布时间 :2019-05-23 11:35:14
基于电镜中心(EMC)FEI电镜数据,材料学院李均钦教授课题组在JCR1区期刊ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces上发表论文,具体如下:
Stacking Fault Induced Minimized Lattice Thermal Conductivity in the HighPerformance GeTe-Based Thermoelectric Materials upon Bi2Te3 Alloying
Junqin Li, Yucheng Xie, Chunxiao Zhang, Kuan Ma, Fusheng Liu, Weiqin Ao, Yu Li, and Chaohua Zhang
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, Just Accepted Manuscript • DOI: 10.1021/acsami.9b04984 • Publication Date (Web): 15 May 2019
Downloaded from http://pubs.acs.org on May 22, 2019
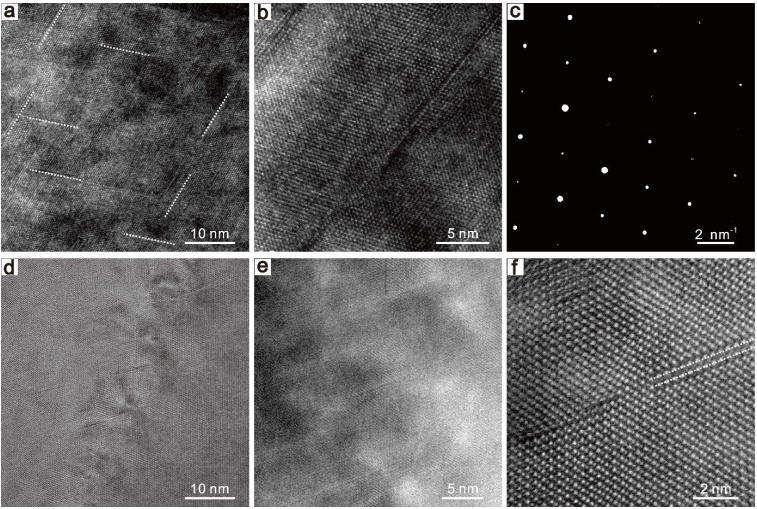
Materials with low lattice thermal conductivity (κlat) are crucial for the applications of thermal insulation and thermoelectric energy conversion. Stacking faults induced phonon scattering within interfaces has been put forward theoretically by Klemens in 1950s. However, unlike other traditional defects like point defects, grain boundaries and dislocations, the role of stacking faults for reducing κlat remains poorly understood and has yet to be revealed experimentally. The layered Bi2Te3 with a van der Wass gap shows different stacking structures than the non-layered GeTe, which is used to introduce stacking faults into the GeTe-based alloys in this work. Based on the experimental and theoretical modeling results, this paper reveals the significant contribution of stacking-fault phonon scattering for minimizing the κlat. Besides the achieved extreme low κlat (~0.39 Wm-1K-1 at 573 K), optimized carrier density and band convergence are also realized in the GeTe-based alloys upon Bi2Te3 alloying, leading to a significant high thermoelectric figure of merit ZT>2 at 773 K and an averaged ZT>1.4 within 300-773 K. This stacking-fault engineering strategy provide a different avenue to reduce the κlat for enhancing the performance of thermal insulation and thermoelectric materials.