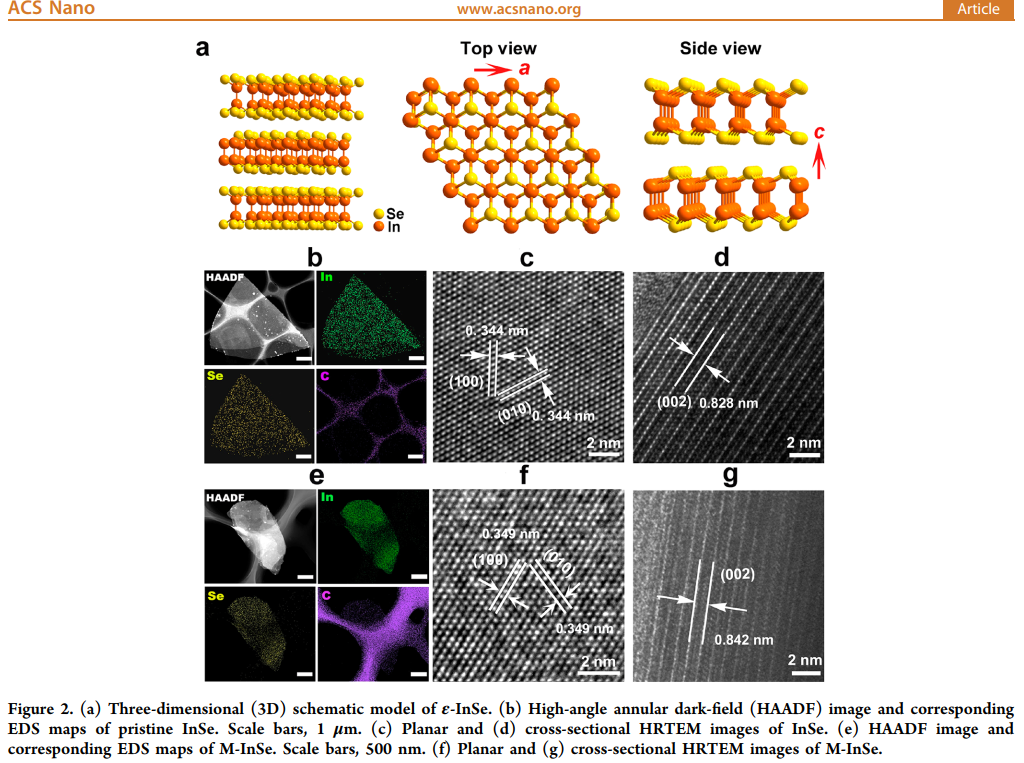
基于电镜中心(EMC)FEI电镜数据,深圳大学张文静教授课题组郝巧燕博士在ACS NANO期刊上发表论文,文章中的超薄InSe纳米片通过本中心球差电镜进行了HAADF、HRTEM以及EDS表征,文章摘要如下:
Surface-Modified Ultrathin InSe Nanosheets with Enhanced Stability and Photoluminescence for High-Performance Optoelectronics
Qiaoyan Hao,# Jidong Liu,# Gang Wang, Jiewei Chen, Haibo Gan, Jiaqi Zhu, Yuxuan Ke, Yang Chai,
Junhao Lin, and Wenjing Zhang*
Indium selenide (InSe) has become a research hotspot because of its favorable carrier mobility and thickness-tunable band gap, showing great application potential in high-performance optoelectronic devices. The trend of miniaturization in optoelec tronics has forced the feature sizes of the electronic components to shrink accordingly. Therefore, atomically thin InSe crystals may play an important role in future optoelectronics. Given the instability and ultralow photoluminescent (PL) emission of mechanically exfoliated ultrathin InSe, synthesis of highly stable mono- and few-layer InSe nanosheets with high PL efficiency has become crucial. Herein,ultrathin InSe nanosheets were preparedviathermal annealing of electrochemically intercalated products from bulk InSe. The size and yield of the as-prepared nanosheets were up to∼160μm and∼70%, respectively, and∼80% of the nanosheets were less thanfive layer. Impressively, the as-prepared nanosheets
showed greatly enhanced stability and PL emission because of surface modification by carbon species. Efficient photoresponsivity of 2 A/W was achieved in the as-prepared nanosheet-based devices. These nanosheets were further assembled into large-area thinfilms with photoresponsivity of 16 A/W and an average Hall mobility of about 5 cm2V-1s-1. Finally, one-dimensional (1D) InSe nanoscrolls with a length up to 90μm were constructed by solvent-assisted self-assembly of the exfoliated nanosheets.、